수정중
❗바킹독님의 실전 알고리즘 강의를 듣고 정리하는 포스팅입니다.
1주차 내용 정리
배열
Python 활용
파이썬에서는 리스트가 배열 기능 제공
- 파이썬의 리스트는 서로 다른 자료형을 원소로 가질 수 있음
- 동적 배열로써 자유롭게 크기 확장 가능
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
# 원소 삽입
arr.append(5)
arr.insert(1, 6) # 1번 인덱스에 6삽입
# 원소 삭제
del[0]
arr.remove(2)
Swift 활용
스위프트에서 제공하는 Array 사용
- 구조체 타입
- 모두 동일한 자료형만 저장 가능
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
var arr: [Int] = [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 원소 삽입
arr.append(4)
arr.insert(6, at:1) // 1번에 6삽입
// 원소 삭제
arr.remove(at: 2)
arr.removeFirst()
arr.popLast() // Optional 반환
arr.removeLast() //Non-Optional 반환
문제풀이
boj 10808번 : 알파벳 개수
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
import sys input = sys.stdin.readline s = input().strip() temp = [0] * 26 for c in s: temp[ord(c) - 97] += 1 print(*temp)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
let s = readLine()!.map { String($0) } var temp: [Int] = Array(repeating: 0, count: 26) for c in s { let idx = Int(UnicodeScalar(c)!.value) - 97 temp[idx] += 1 } print(temp.map{ String($0) }.joined(separator: " "))
https://developer-p.tistory.com/192 : swift ascii 다루기
boj 2577 : 숫자의 개수
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
import sys input = sys.stdin.readline a = int(input()) b = int(input()) c = int(input()) s = str(a * b * c) temp = [0] * 10 for c in s: temp[int(c)] += 1 for i in temp: print(i)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
let a = Int(readLine()!)! let b = Int(readLine()!)! let c = Int(readLine()!)! let s = String(a * b * c).map{ String($0) } var temp: [Int] = Array(repeating: 0, count: 10) for c in s { temp[Int(c)!] += 1 } for i in temp { print(i) }
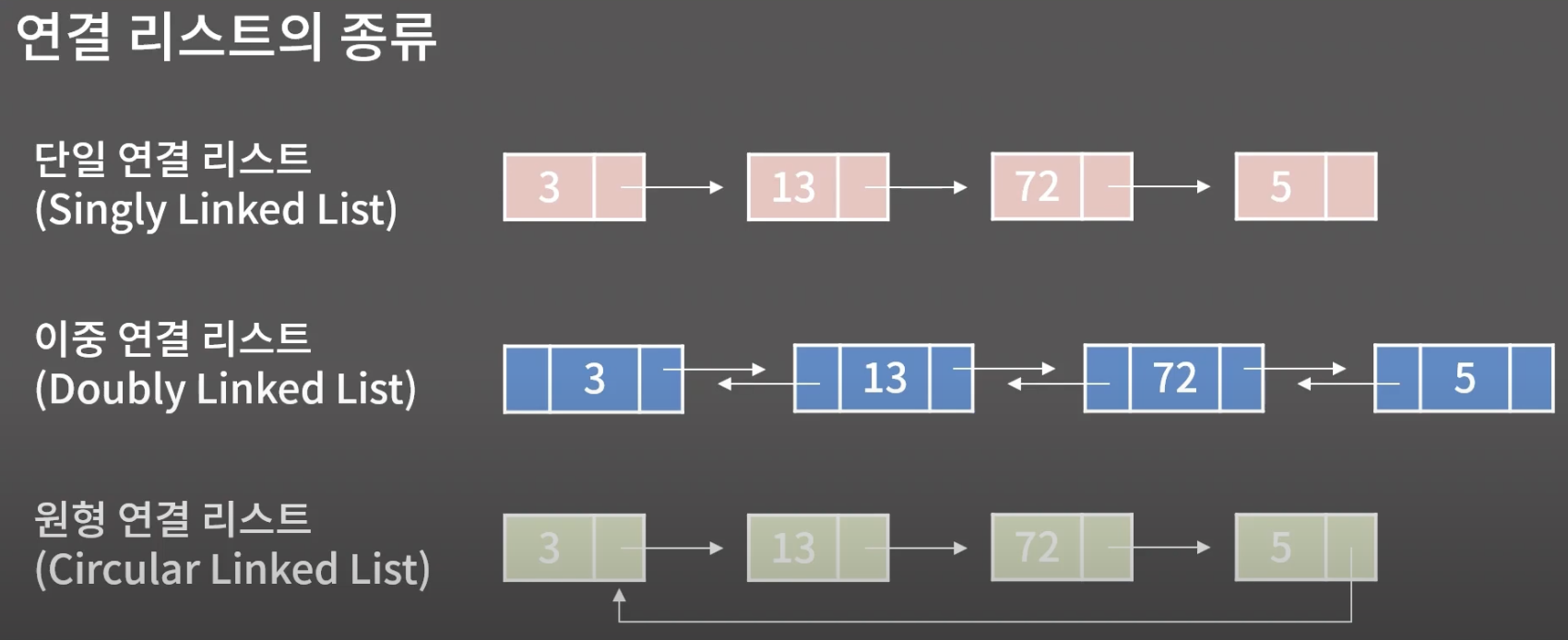
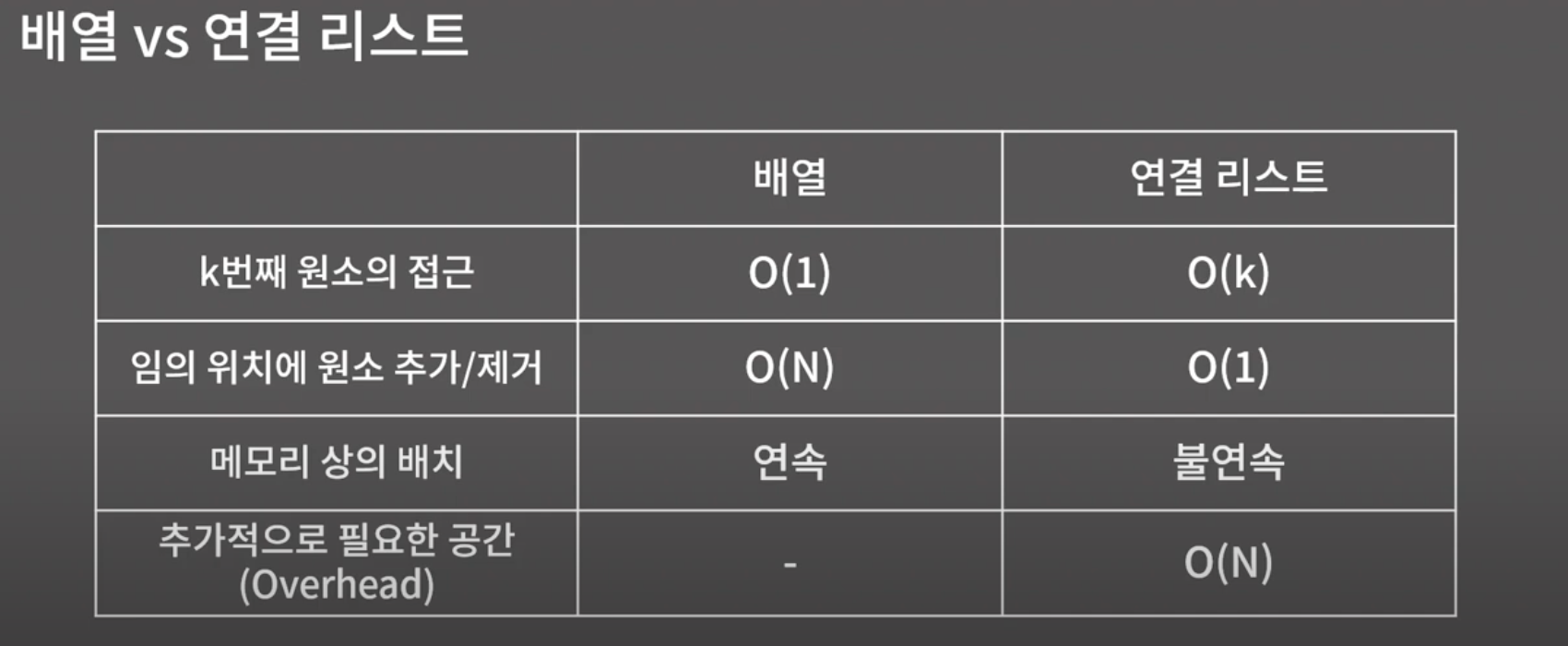
연결 리스트
: 원소를 저장할 때 그 다음 원소가 있는 위치를 포함하여 저장하는 자료구조 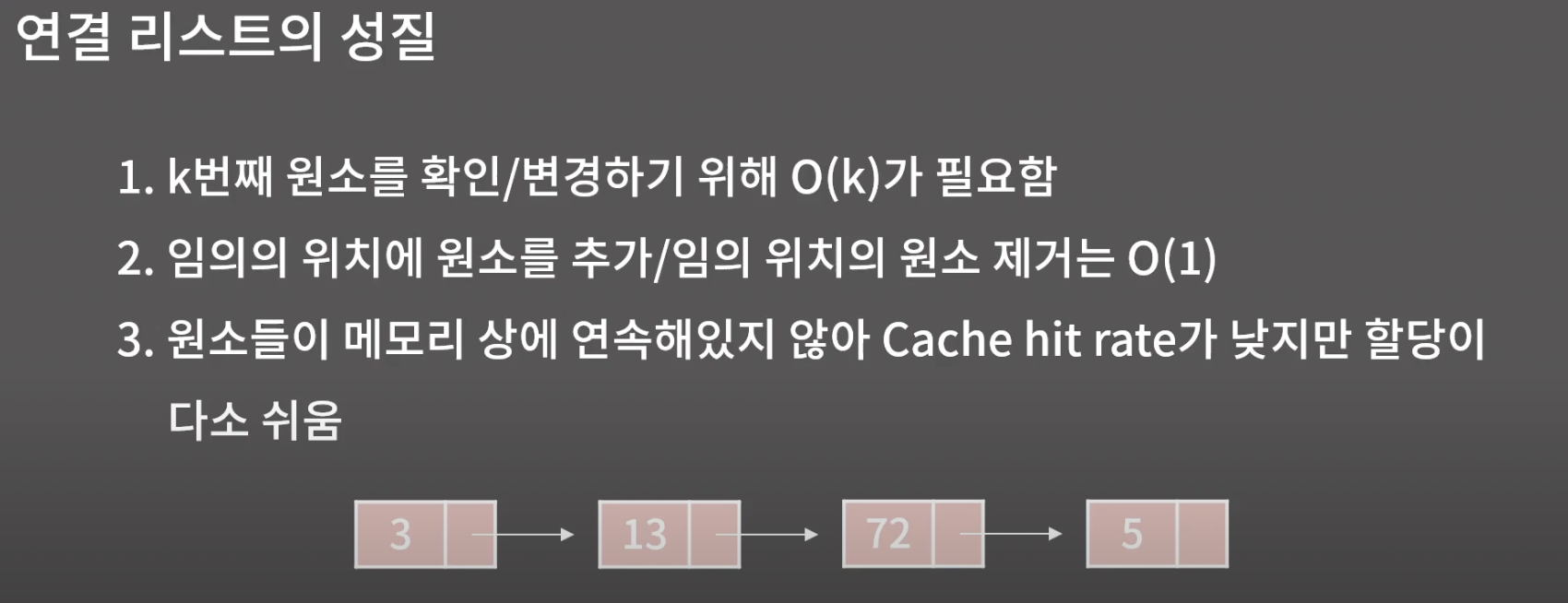
Python 활용
- 리스트에 연결 리스트 기능까지 구현되어 있음(배열 이어붙이기, 중간 삽입, 삭제 등)
Swift 활용
- …
연습문제
boj1406
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
import sys input = sys.stdin.readline s = list(input().strip()) m = int(input()) cur = len(s) for _ in range(m): temp = list(input().strip().split()) command = temp[0] if len(temp) > 1: s.insert(cur, temp[1]) cur += 1 elif command == "L": if cur > 0: cur -= 1 elif command == "D": if cur < len(s): cur += 1 elif command == "B": if cur > 0: del s[cur-1] cur -= 1 print("".join(s)) # 시간초과 # 리스트가 연결 리스트 기능 제공한다며!!!!! 외않대?
1
스택
: 한 쪽 끝에서만 원소를 넣거나 뺄 수 있는 FILO 구조 
Python 활용
- 별도의 스택 자료구조는 없지만 리스트로 동일하게 사용 가능
Swift 활용
- …
문제풀이
boj 10828 : 스택
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
import sys input = sys.stdin.readline n = int(input()) stack = [] pos = 0 for i in range(n): temp = list(input().strip().split()) if temp[0] == 'push': stack.append(temp[1]) pos += 1 elif temp[0] == 'pop': if pos > 0: print(stack.pop()) pos -= 1 else: print(-1) elif temp[0] == 'size': print(pos) elif temp[0] == 'empty': if pos == 0: print(1) else: print(0) elif temp[0] == 'top': if pos == 0: print(-1) else: print(stack[pos-1])
1
큐
Python 활용
- queue 자료구조가 별도로 존재하지만 그냥 deque으로 한 번에 쓰고 싶음..
Swift 활용
- …
문제풀이
boj 10845 : 큐
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
import sys from collections import deque input = sys.stdin.readline n = int(input()) queue = deque([]) head = 0 tail = 0 for i in range(n): temp = list(input().strip().split()) if temp[0] == 'push': queue.append(temp[1]) tail += 1 elif temp[0] == 'pop': if head < tail: print(queue.popleft()) head += 1 else: print(-1) elif temp[0] == 'size': print(tail - head) elif temp[0] == 'empty': if head == tail: print(1) else: print(0) elif temp[0] == 'front': if head == tail: print(-1) else: print(queue[0]) elif temp[0] == 'back': if head == tail: print(-1) else: print(queue[-1])
덱
Python 활용
- from collections import deque 통해 사용 가능
Swift 활용
- …
문제풀이
boj 10866 : 덱
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46
import sys from collections import deque input = sys.stdin.readline n = int(input()) queue = deque([]) head = 0 tail = 0 for i in range(n): temp = list(input().strip().split()) if temp[0] == 'push_back': queue.append(temp[1]) tail += 1 elif temp[0] == 'push_front': queue.appendleft(temp[1]) head -= 1 elif temp[0] == 'pop_front': if head < tail: print(queue.popleft()) head += 1 else: print(-1) elif temp[0] == 'pop_back': if head < tail: print(queue.pop()) tail -= 1 else: print(-1) elif temp[0] == 'size': print(tail - head) elif temp[0] == 'empty': if head == tail: print(1) else: print(0) elif temp[0] == 'front': if head == tail: print(-1) else: print(queue[0]) elif temp[0] == 'back': if head == tail: print(-1) else: print(queue[-1])
스택의 활용
: 스택 구조를 활용하여 괄호의 쌍이 올바른지 판단하는 문제 해결
연습문제
boj 4949 : 균형잡힌 세상
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
while True: s = input() stack = [] if s == ".": break for c in s: if c == "(" or c == "[": stack.append(c) elif c == ")": if not stack or stack[-1] != "(": stack.append(c) break stack.pop() elif c == "]": if not stack or stack[-1] != "[": stack.append(c) break stack.pop() if stack: print("no") else: print("yes")